Exploring the Causes of Periodontal Disease: Is it Contagious or Hereditary?
Whether periodontal disease is contagious or hereditary is a common question from patients sent to Home Dentistry because this pathology is quite common but progresses silently and leaves serious consequences. The following information will help clarify this issue.

What is Periodontal Disease and What are Its Potential Causes?
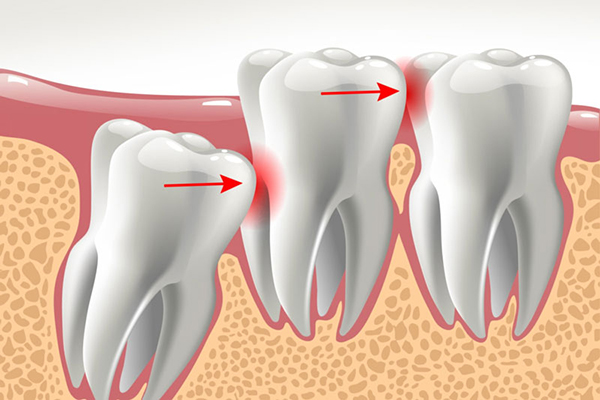
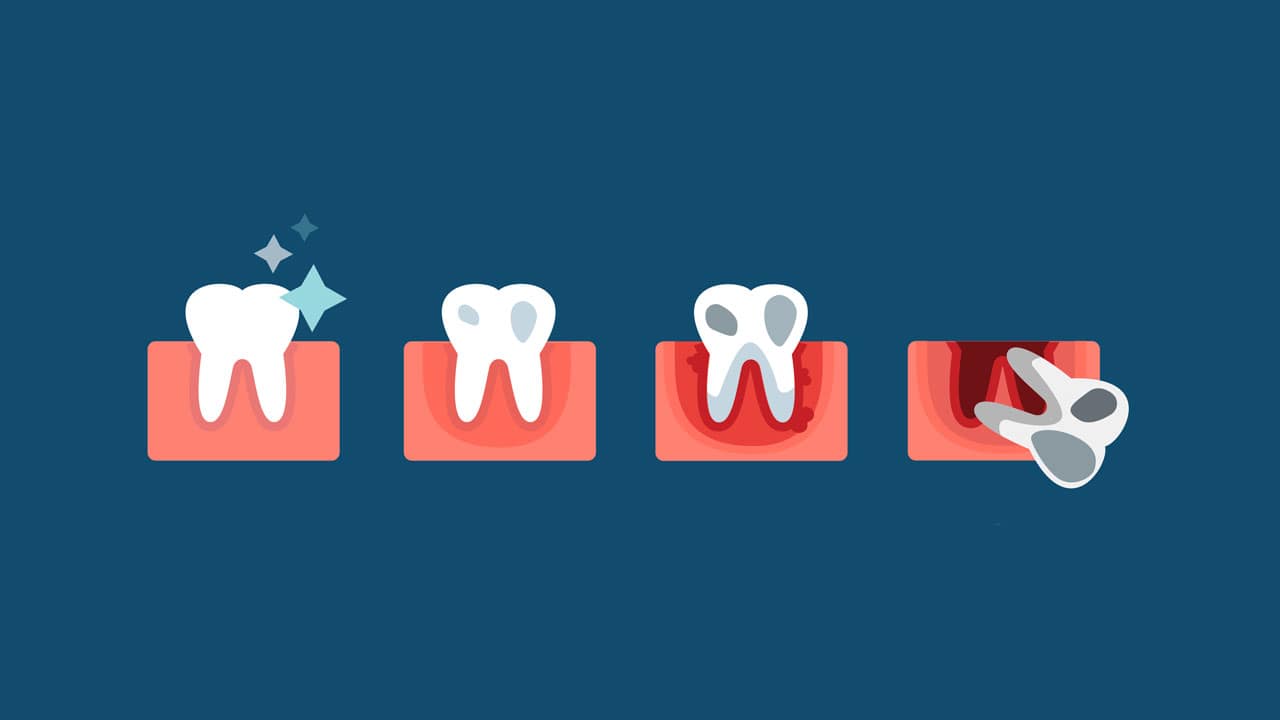
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common condition that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. If you are experiencing symptoms of periodontal disease, such as bleeding gums, bad breath, or loose teeth, it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent further damage to your oral health. When left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems.
There are several possible causes of periodontal disease, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, genetics, and certain medical conditions.
- Poor oral hygiene, such as infrequent brushing and flossing, can lead to the buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth and gums, which can eventually cause inflammation and infection.
- Smoking can also contribute to periodontal disease by reducing blood flow to the gums and impairing the immune system’s ability to fight off infections.
- Genetics may also play a role in the development of periodontal disease, as some people may be more susceptible to the condition due to inherited traits.
- Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of developing gum disease. Other risk factors for periodontal disease include hormonal changes, certain medications, and a diet high in sugar and carbohydrates.
In addition to these potential causes, poor lifestyle choices can also increase the risk of developing periodontal disease. Stress, lack of sleep, and poor nutrition can all have a negative impact on oral health and increase the likelihood of gum disease.
How Far Does Contagion Spread for Periodontal Disease?
While proper oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings can help prevent and treat Periodontal diseases, a common question is whether they are contagious and can spread between people.
According to dental research, gum diseases are not contagious in the sense that they can directly spread from person to person through saliva or close contact. However, the same risk factors that lead to gum disease in one person, such as plaque buildup, gum inflammation, and a compromised immune system, can also put others at risk.
In other words, periodontal disease itself is not contagious, but the underlying conditions and risk factors that enable the disease are common to groups of people with a similar lifestyle and environment. By practicing good oral hygiene and avoiding bad habits like smoking, individuals can lower their risk and reduce the chances of ‘catching’ gum disease from those around them. While periodontitis cannot spread directly between humans, its risk factors can spread in a sense through behaviors and environments, highlighting the importance of individual dental health and responsibility.
The Role of Heredity in Developing and Passing on Gum Disease
While gum diseases are not directly contagious, hereditary factors can play a role in their development and transmission between family members. Some people may be genetically predisposed to excessive inflammation or a weakened immune response to plaque buildup, increasing their risk of periodontitis. Studies of twins and families suggest that up to half of the variation in gum disease risk can be attributed to inherited genes. However, genetics are not destiny, and even those with a family history can maintain healthy gums with diligent oral hygiene, regular dental exams, and addressing any modifiable risk factors under their control.
How to effectively prevent periodontitis
Not only causes tooth loss, pain, swelling, bad breath, difficulty eating. Periodontitis also has many other dangerous complications such as facial pain, cardiovascular disease, bacteremia, diabetes, respiratory disease, low birth weight premature …
Therefore, to effectively prevent this disease, we need to prevent plaque formation according to the following rules:
– Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste for strong teeth and soft bristles.
– The edges of the teeth are where plaque forms and accumulates, so you need to pay special attention to this area by brushing your teeth vertically and placing the brush at a 45 degree angle to fully clean.
– Use dental floss to clean plaque between teeth.
– Limit eating foods high in sugar and acid such as candy, soft drinks before bedtime.
– Develop the habit of rinsing your mouth with salt water or mouthwash after light meals.
Dental checkups every 6 months for the dentist to scale your teeth and clean your mouth.